🇬🇧 – 🇮🇹
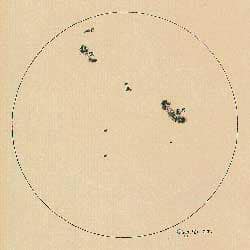
In 1587 Johannes Fabricius was born; a German physician, astrologer and astronomer of Frisian ethnicity, the eldest son of David Fabricius among the first to have observed through a telescope sunspots, the discovery of which Galileo Galilei (whose sunspot drawing we see) would also come to almost simultaneously.
Nel 1587 nasce Johannes Fabricius un medico, astrologo e astronomo tedesco di etnia frisona, primogenito di David Fabricius tra i primi ad aver osservato attraverso un telescopio le macchie solari, alla cui scoperta sarebbe giunto quasi contemporaneamente anche Galileo Galilei (di cui vediamo il disegno delle macchie solari).
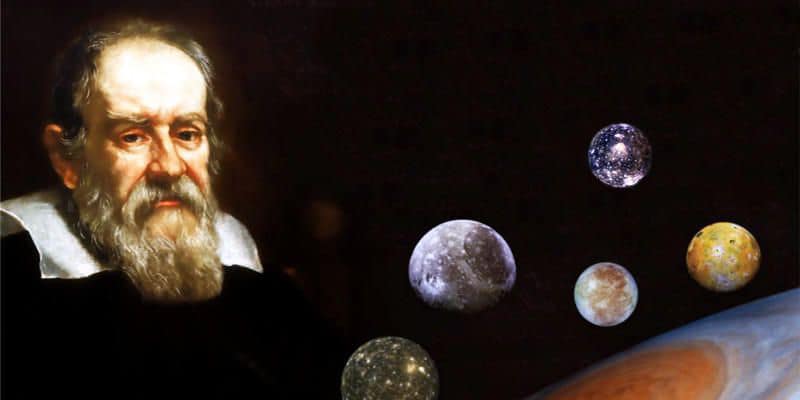
In 1642 in Arcetri, near Florence, the great astronomer and physicist Galileo Galilei (see image), considered the father of modern science, died. A key figure in the scientific revolution for explicitly introducing the scientific method (also called the “Galilean method” or “experimental method”), his name is associated with important contributions in physics and astronomy. Also of primary importance was his role in the astronomical revolution, with his support for the heliocentric system and Copernican theory.
Nel 1642 ad Arcetri, vicino a Firenze, muore il grande astronomo e fisico Galileo Galilei (vedi immagine), considerato il padre della scienza moderna. Personaggio chiave della rivoluzione scientifica, per aver esplicitamente introdotto il metodo scientifico (detto anche “metodo galileiano” o “metodo sperimentale”), il suo nome è associato a importanti contributi in fisica e in astronomia. Di primaria importanza fu anche il ruolo svolto nella rivoluzione astronomica, con il sostegno al sistema eliocentrico e alla teoria copernicana.

In 1838 Alfred Vail demonstrated the operation of the telegraph (see photo) using dots and dashes (this is the predecessor of Morse Code)
Nel 1838 Alfred Vail dimostra il funzionamento del telegrafo (vedi foto) usando puntini e lineette (è il predecessore del Codice Morse)
In 1868 English astronomer Frank Watson Dyson, known for introducing the Greenwich hour signal and for the role he played in verifying Einstein’s theory of relativity, was born. His name is also remembered for his numerous studies of solar eclipses; he was an authority in the field of solar corona and chromosphere spectroscopy.
Nel 1868 nasce l’astronomo inglese Frank Dyson noto per aver introdotto il segnale orario di Greenwich e per il ruolo giocato nel verificare la teoria della relatività di Einstein. Il suo nome è ricordato altresì per i numerosi studi sulle eclissi solari; è stato un’autorità nel campo della spettroscopia della corona solare e della cromosfera.

In 1918 William E. Gordon, electrical engineer, physicist, and astronomer, was born. He has been called the “father of the Arecibo Observatory” (see before-and-after image of the observatory,on December 1 2020, the suspended structure above broke loose from the support cables, falling and destroying the primary reflector)
Nel 1918 nasce William E. Gordon, un ingegnere elettrico, fisico e astronomo. È stato definito il “padre dell’Osservatorio di Arecibo” (vedi immagine del prima e dopo dell’osservatorio, il 1º dicembre 2020 la struttura sospesa sovrastante si è staccata dai cavi di supporto, cadendo e distruggendo il riflettore primario).
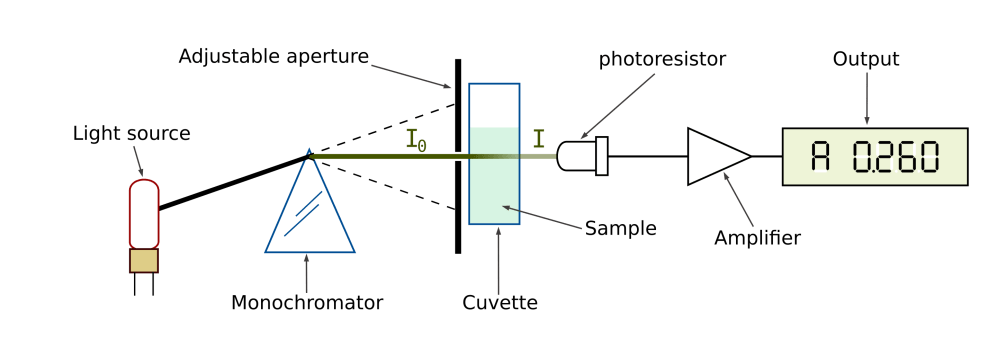
In 1935-Arthur Cobb Hardy patented the spectrophotometer (see graphic) to study electromagnetic spectra, specifically visible light, from near ultraviolet to near infrared.
Nel 1935 Arthur Cobb Hardy brevetta lo spettrofotometro (vedi grafico) per studiare gli spettri elettromagnetici, nello specifico la luce visibile, dal vicino ultravioletto al vicino infrarosso.
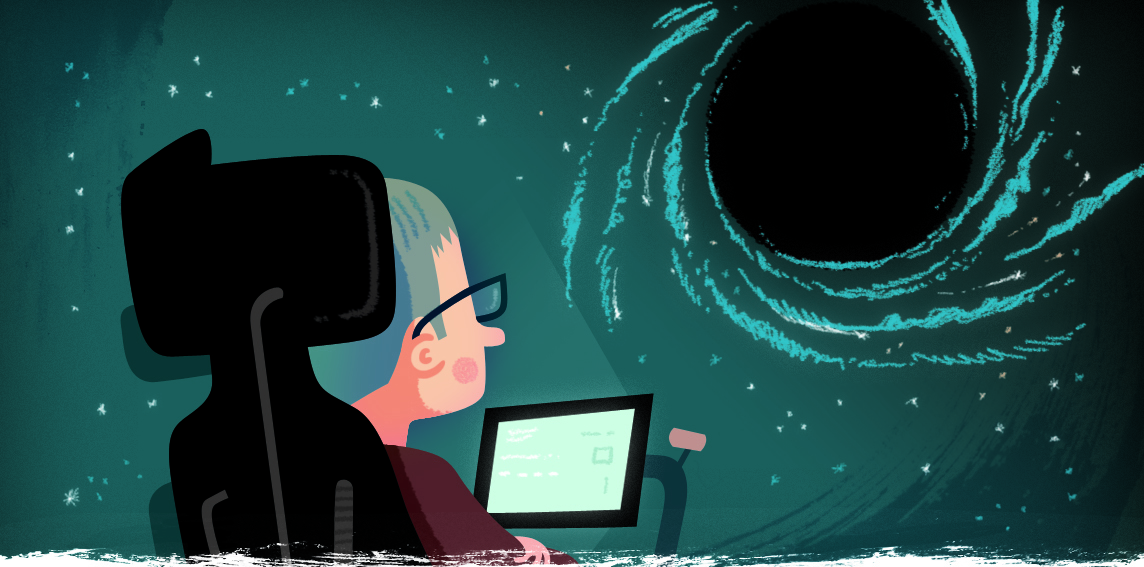
In 1942, the great Stephen Hawking, a British cosmologist, physicist, mathematician, astrophysicist, academic and popularizer of science, was born; he is among the world’s most influential and well-known theoretical physicists, best known for his studies on black holes, quantum cosmology and the origin of the universe; he is remembered for Hawking radiation, the cosmological theory of the boundless beginning of the universe (called the Hartle-Hawking state) and the thermodynamics of black holes. Fruitful collaboration with other scientists has contributed to the development of numerous physical and astronomical theories: the multiverse, galactic formation and evolution, and cosmic inflation; always explained with clarity and simplicity, they have reached the general public through numerous popular science texts.
Nel 1942 nasce il grande Stephen Hawking, un cosmologo, fisico, matematico, astrofisico, accademico e divulgatore scientifico britannico, fra i più autorevoli e conosciuti fisici teorici al mondo, noto soprattutto per i suoi studi sui buchi neri, sulla cosmologia quantistica e sull’origine dell’universo; viene ricordato per la radiazione di Hawking, la teoria cosmologica sull’inizio senza confini dell’universo (denominata stato di Hartle-Hawking) e la termodinamica dei buchi neri. La fruttuosa collaborazione con altri scienziati ha contribuito all’elaborazione di numerose teorie fisiche e astronomiche: il multiverso, la formazione ed evoluzione galattica e l’inflazione cosmica; sempre spiegate con chiarezza e semplicità, hanno raggiunto il grande pubblico attraverso numerosi testi di divulgazione scientifica.
In 1998 Saul Perlmutter, along with scientists Brian P. Schmidt and Adam Riess, announced the discovery that the universe is in a phase of continuous accelerated expansion.
Nel 1998 Saul Perlmutter, insieme agli scienziati Brian P. Schmidt e Adam Riess, annuncia la scoperta secondo cui l’universo sarebbe in una fase di continua espansione accelerata.
Text source: Wikipedia
Sostieni anche tu Wikipedia
Google translate