🇬🇧 – 🇮🇹
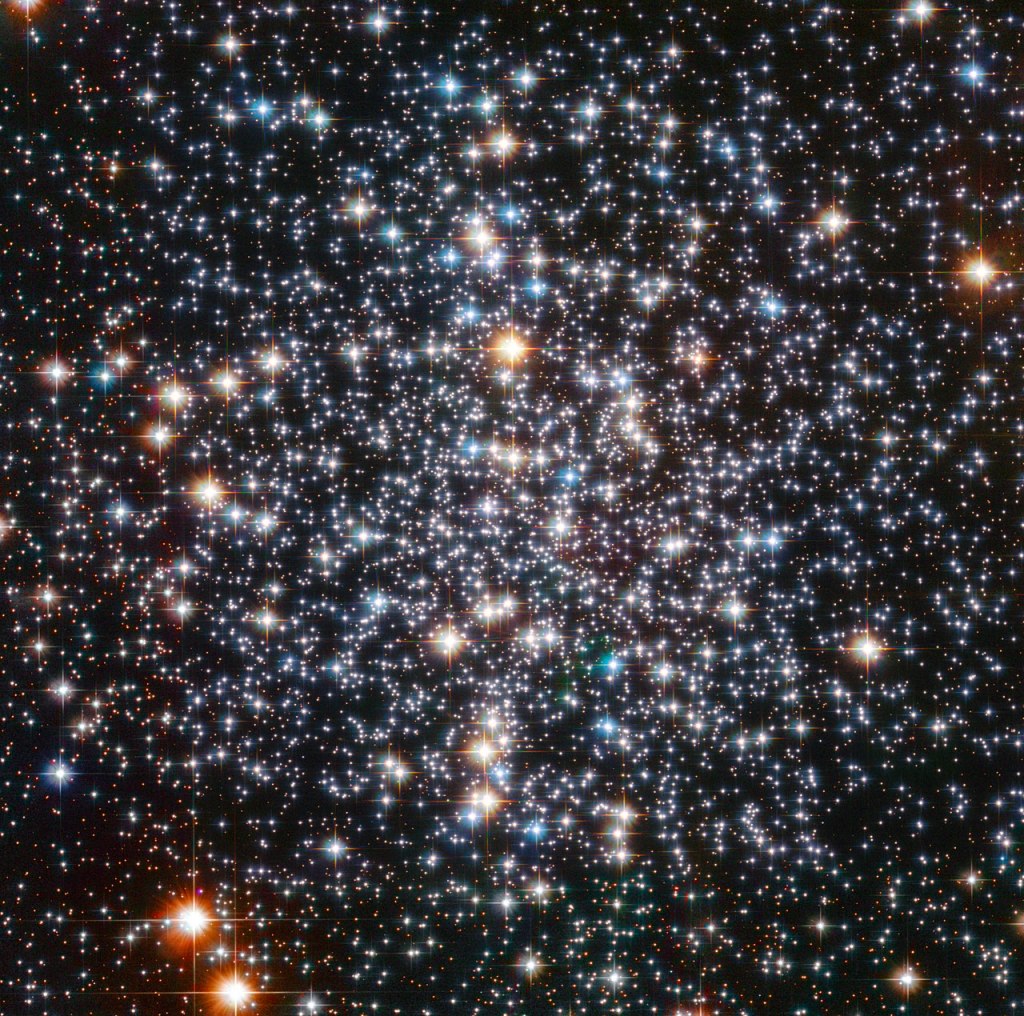

In 1764, the astronomer Charles Messier cataloged the brilliant globular cluster M4 in the constellation of Scorpius (click on M4 to find out more).
Nel 1764 l’astronomo Charles Messier cataloga il brillante ammasso globulare M4 nella costellazione dello Scorpione (clicca su M4 per saperne di più).
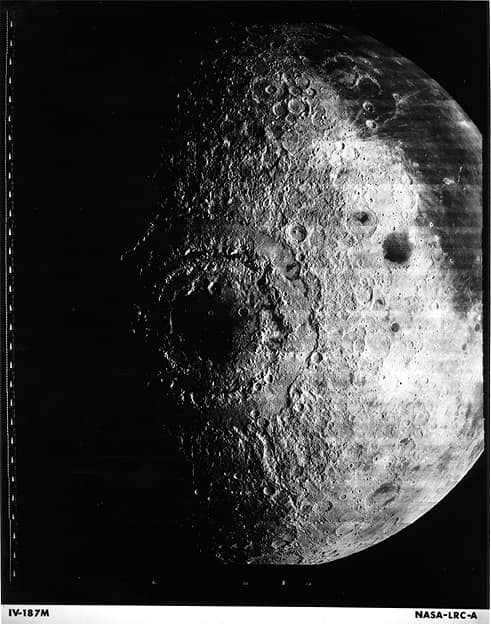
In 1967, the lunar satellite Lunar Orbiter 4 entered the orbit of the Moon and began taking photographs three days later
Nel 1967 il satellite lunare Lunar Orbiter 4 si inserisce nell’orbita della Luna e tre giorni dopo inizia le riprese fotografiche
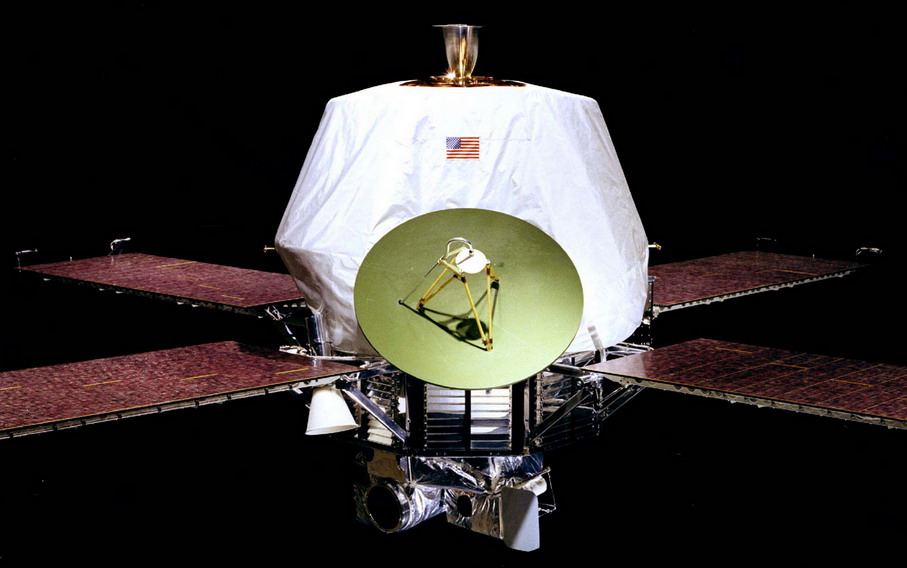
In 1971 NASA launches the Mariner 8 probe with the Atlas-Centaur SLV-3C rocket (see photo) with the aim of reaching the orbit of Mars but the launch fails and falls into the Atlantic Ocean
Nel 1971 la NASA lancia la sonda Mariner 8 con con il razzo Atlas-Centaur SLV-3C (vedi foto) con lo scopo di raggiungere l’orbita di Marte ma il lancio fallisce e cade nell’oceano Atlantico
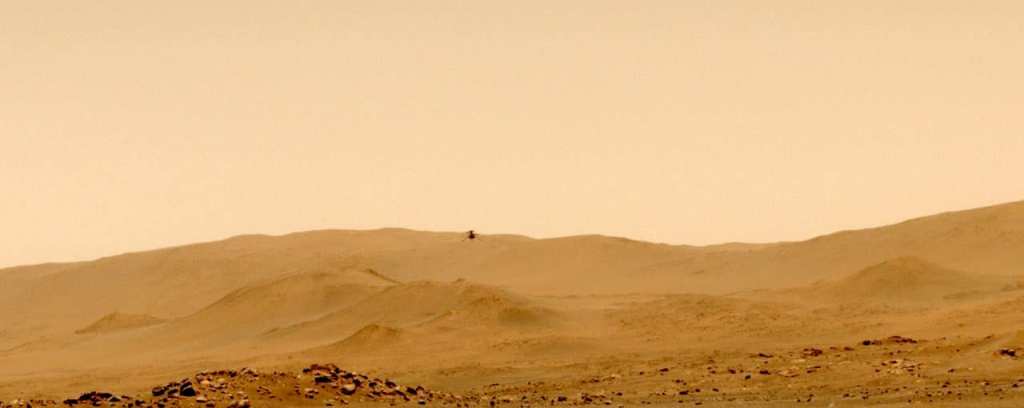


At 01:31 in 2021 was the fifth flight of the Ingenuity helicopter to Mars (see photo above) with its first one-way trip from Wright Brothers Field to an airfield 129 meters to the south. Upon arriving above its new airfield, Ingenuity climbed up to 10 meters and captured high-resolution color images of its new base before landing. Among its objectives: aerial observations of areas not accessible by a rover and detailed stereo images from atmospheric altitudes. The flight started at 15:26. EDT (12:26 pm PDT, 12:33 pm Mars local time) and lasted 108 seconds. The Ingenuity team chose the new landing site based on information gathered during the previous flight – the first “aerial survey” operation on another world – which allowed them to generate digital elevation maps indicating almost completely flat terrain almost without obstacles. Videos: https://youtu.be/PFbzEM8PzHE…
Nel 2021 alle 01:31 avviene il quinto volo dell’elicottero Ingenuity su Marte (vedi foto sopra) con il suo primo viaggio di sola andata dal Wright Brothers Field, aeroporto 129 metri a sud. Ingenuity è poi salito fino a 10 metri e ha catturato immagini a colori ad alta risoluzione della sua nuova base prima dell’atterraggio. Tra i suoi obiettivi: osservazioni aeree di aree non accessibili da un rover e immagini stereo dettagliate da altitudini atmosferiche. Il volo è iniziato alle 15:26. EDT (12:26 PDT, 12:33 ora locale di Marte) ed è durato 108 secondi. Il team Ingenuity ha scelto il nuovo sito di atterraggio sulla base delle informazioni raccolte durante il volo precedente – la prima operazione di “rilevamento aereo” su un altro mondo – che ha permesso loro di generare mappe digitali di elevazione che indicavano un terreno quasi completamente pianeggiante e quasi privo di ostacoli. Video: https://youtu.be/PFbzEM8PzHE…
Sostieni anche tu Wikipedia
Text source: Wikipedia, Nasa
Google translate
