🇬🇧 – 🇮🇹

In 1687, Geminiano Montanari died, an Italian astronomer known for the discovery of a comet and who was the first to report the variability of the star Algol in 1668 (see celestial map), the beginning of the modern systematic study of the variations in the brightness of stars. In his frequent polemics he vigorously demolished several antiquated doctrines: first of all that of astrological influences.
Nel 1687 muore Geminiano Montanari, astronomo italiano noto per la scoperta di una cometa e per primo segnalò nel 1668 la variabilità della stella Algol (vedi mappa celeste), inizio del moderno studio sistematico delle variazioni di splendore delle stelle. Nelle sue frequenti polemiche demolì con vigore parecchie dottrine antiquate: prima tra tutte quella delle influenze astrologiche.
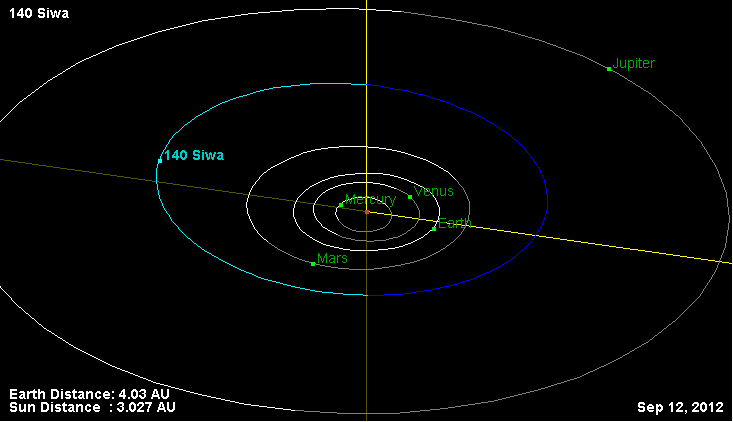
In 1874 the astronomer Johann Palisa discovered the asteroid 1948 AL and named it 140 Siwa, a large, dark main belt asteroid; it has a very flat light curve, which would indicate an almost spherical body. Its composition is that of a P-type (or probably C-type) asteroid, the spectral classification can be seen here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Asteroid_spectral_types
Nel 1874 l’astronomo Johann Palisa scopre l’asteroide 1948 AL e lo battezza 140 Siwa, un grande e scuro asteroide della fascia principale; possiede una curva di luce molta piatta, che indicherebbe un corpo pressoché sferico. La sua composizione è quella di una asteroide di tipo P (o probabilmente di tipo C), la classificazione spettrale la si può vedere qui: https://it.m.wikipedia.org/…/Classificazione_spettrale….

In 1884, the one that passes through the Greenwich Observatory was adopted as the Zero Meridian (see photo).
Nel 1884 viene adottato come Meridiano Zero (vedi foto) quello che passa per il Greenwich Observatory.

In 1892 206P/Barnard-Boattini (see photo) was discovered by Edward Emerson Barnard, a periodic comet of the Solar System, belonging to the family of Jovian comets. It was the first comet to be discovered by photography. The rediscovery of the comet in 2008 by Andrea Boattini was made possible by new digital technologies. In fact, the comet appeared fainter than at the time of its first discovery and suggests that in 1892 the comet was in an outburst phase. The reduced brightness of the comet can be attributed both to its small size and to an excessive reduction in the content of volatile materials in the nucleus following a long history of transits in the inner solar system.
Nel 1892 scoperta da Edward Emerson Barnard la 206P/Barnard-Boattini (vedi foto) una cometa periodica del Sistema solare, appartenente alla famiglia delle comete gioviane. Fu la prima cometa ad essere scoperta per mezzo della fotografia. La riscoperta della cometa nel 2008 da Andrea Boattini è stata resa possibile dalle nuove tecnologie digitali. La cometa infatti è apparsa più debole che non al momento della sua prima scoperta e fa supporre che nel 1892 la cometa fosse in una fase di outburst. La ridotta luminosità della cometa può essere attribuita sia a dimensioni ridotte sia ad un’eccessiva riduzione del contenuto di materiali volatili del nucleo in seguito ad una lunga storia di transiti nel sistema solare interno.

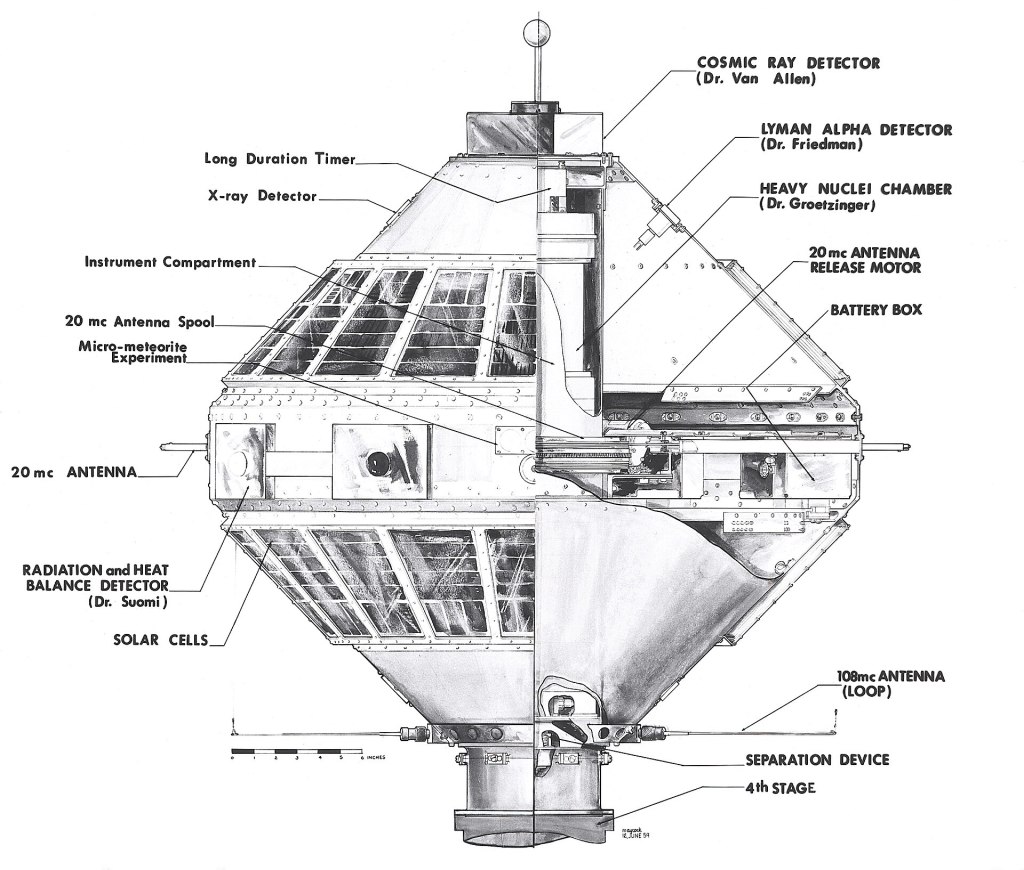
In 1959 Explorer 7 was launched (see photo) to study solar X-rays, the Lyman-alpha flux, energetic particles and cosmic rays.
Nel 1959 lancio dell’Explorer 7 (vedi foto) per studiare raggi X solari, del flusso Lyman-alpha, delle particelle energetiche e dei raggi cosmici.

In 1969, the first rendezvous of three spacecraft: Soyuz 6, Soyuz 7 and Soyuz 8. The planned docking failed
Nel 1969 primo rendezvous di tre navicelle spaziali: Soyuz 6, Soyuz 7 e Soyuz 8. L’aggancio programmato fallisce
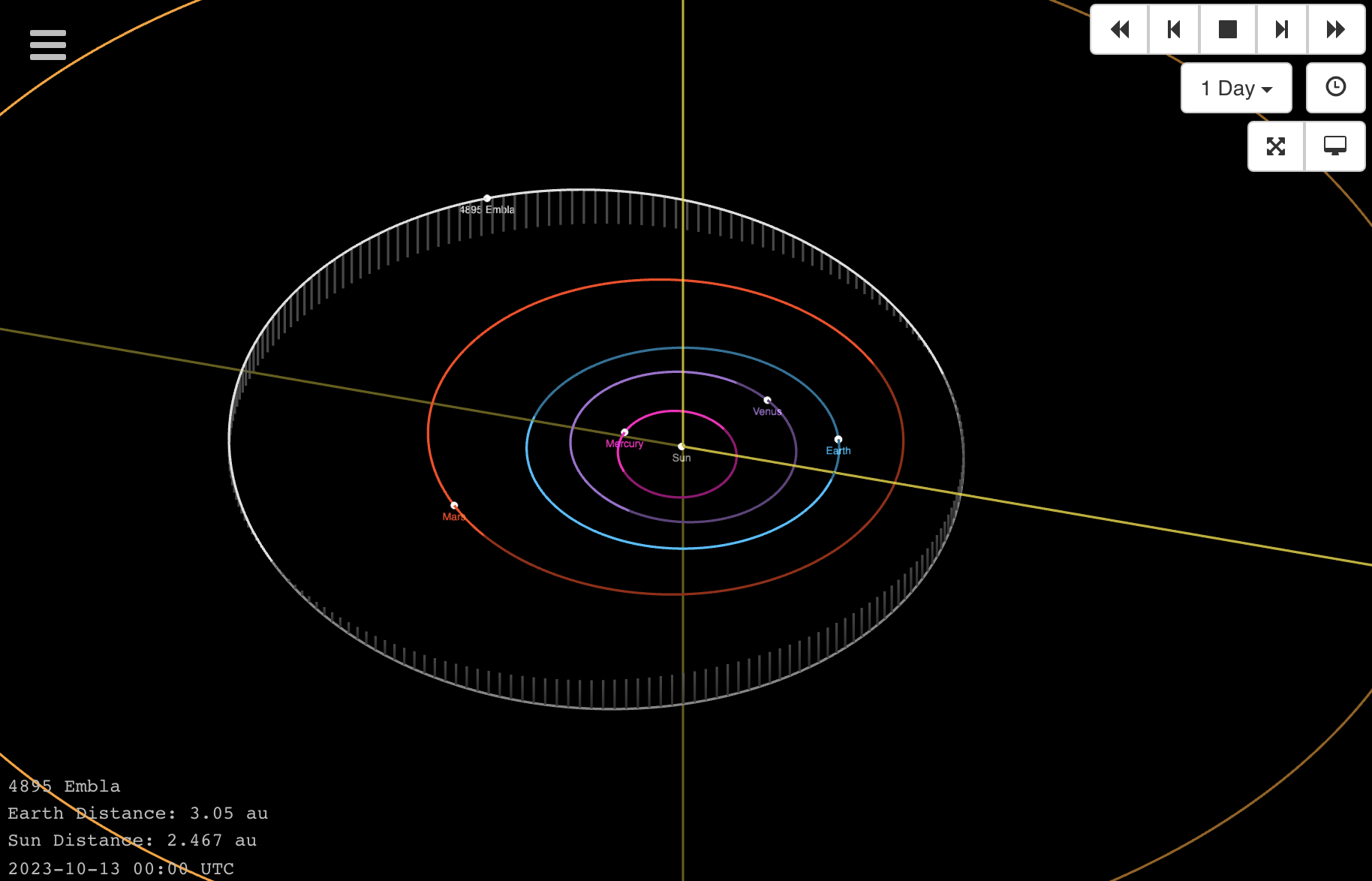
In 1986 Poul Jensen discovered the main belt asteroid 1986 TK4 and christened it “4895 Embla”. Observe the position: https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/sbdb_lookup.html#/?sstr=4895&view=VOP
Nel 1986 Poul Jensen scopre l’asteroide 1986 TK4 della fascia principale e lo battezza “4895 Embla”. Teniamolo d’occhio: https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/sbdb_lookup.html#/?sstr=4895&view=VOP
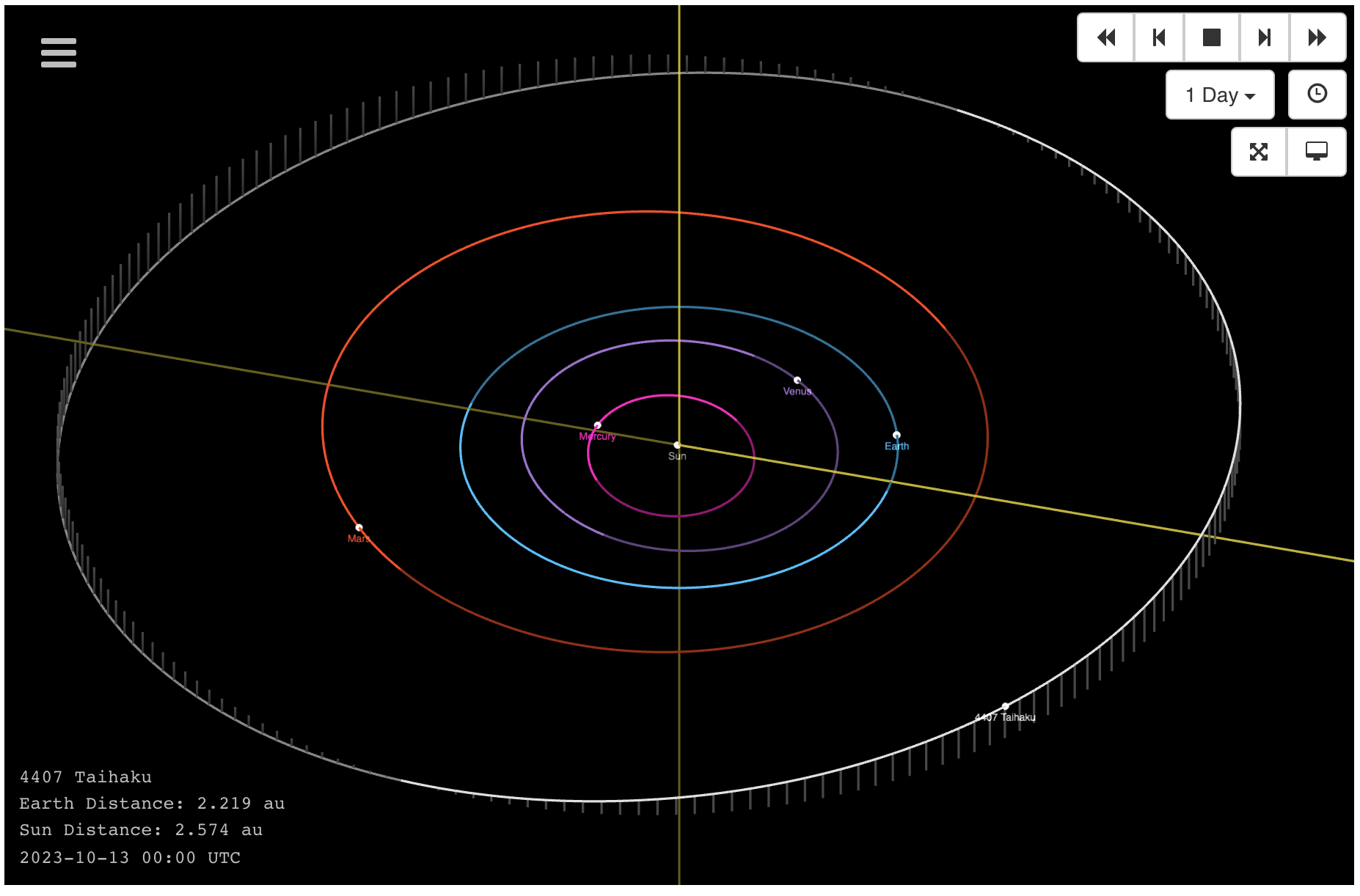
In 1988 Masahiro Koishikawa discovered the main belt asteroid 1988 TF1 and named it “4407 Taihaku”.
Nel 1988 Masahiro Koishikawa scopre l’asteroide della fascia principale 1988 TF1 e lo battezza “4407 Taihaku”.
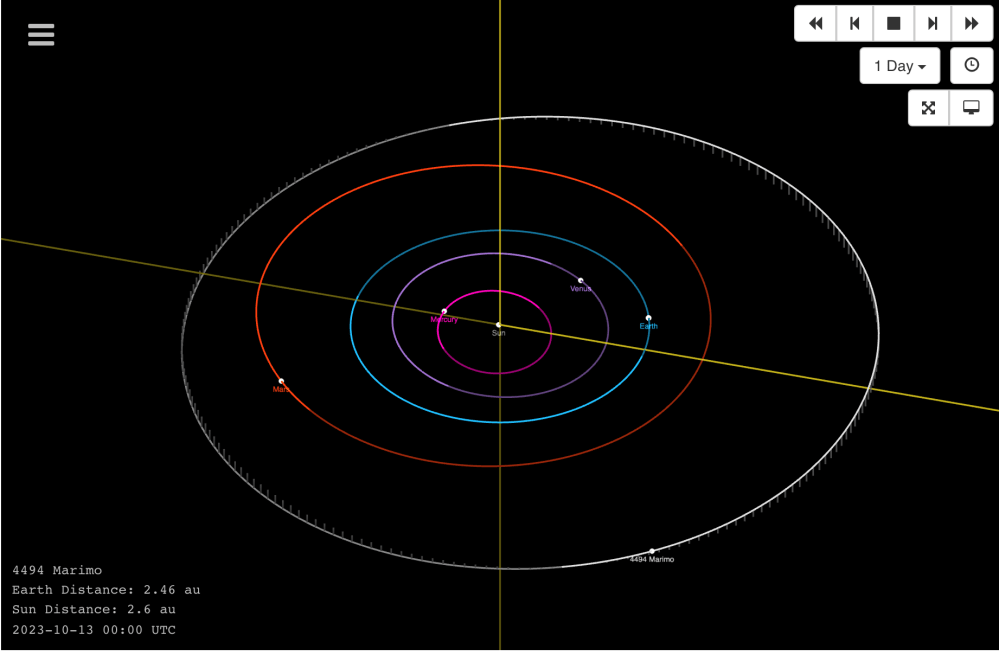
In 1988 Seiji Ueda and Hiroshi Kaneda discovered the main belt asteroid 1988 TK1 and named it “4494 Marimo”. The asteoid is dedicated to a green alga, Aegagropila linnaei, which grows in Lake Akan located on the island of Hokkaidō.
Nel 1988 Seiji Ueda e Hiroshi Kaneda scoprono l’asteroide della fascia principale 1988 TK1 e lo battezzano “4494 Marimo”. L’asteoide è dedicato ad un’alga verde, Aegagropila linnaei, che cresce nel lago Akan situato nell’isola di Hokkaidō.
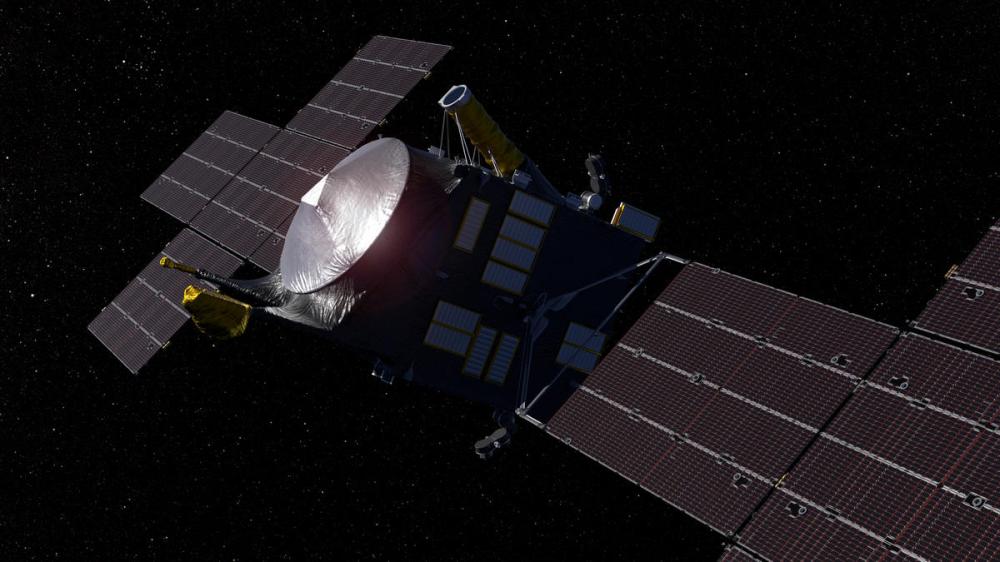
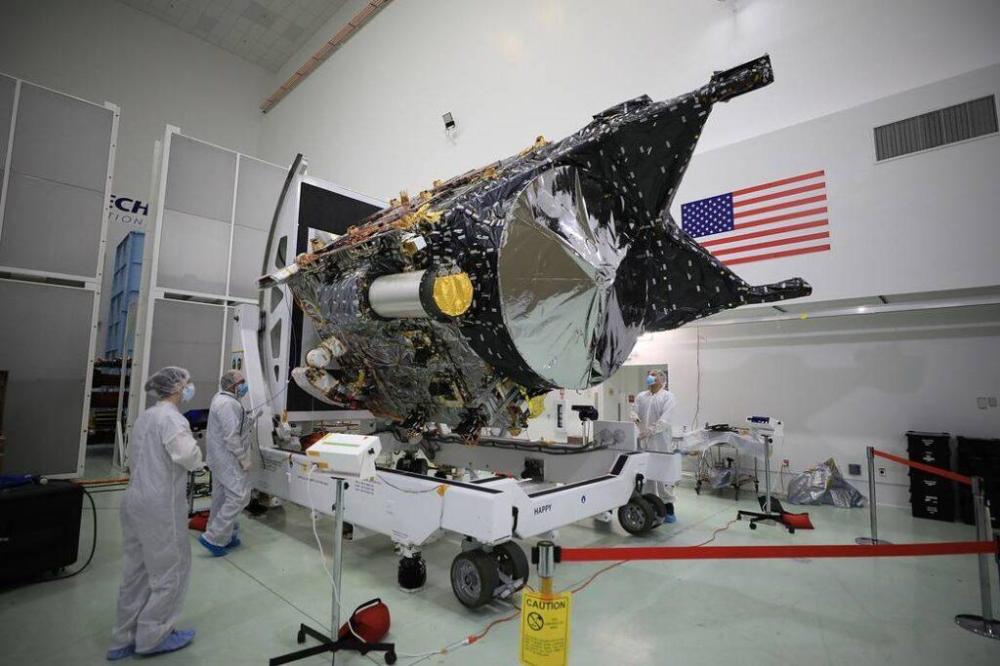


The launch of Psyche, a NASA (JPL + Arizona State University) mission, which will visit the main belt asteroid 16 Psyche after a 4-year journey (flyby with Mars expected in 2026), is scheduled for 2023. The asteroid, composed mainly of iron and nickel, is suspected of being the remnant of the nucleus of an ancient planet, interesting for understanding the formation and evolution of our solar system. Also on board 30 kg of scientific instrumentation including Escape and Plasma Acceleration+ Dynamics Explorers (EscaPADE) which will study the Martian atmosphere, Janus, which will study binary asteroids, a multispectral camera to distinguish metals and silicates, gamma ray and neutron spectrometer for surface mapping, antenna and magnetometer.
Nel 2023 alle ore 16:19 è previsto il lancio di Psyche, una missione NASA (JPL + Arizona State University), che visiterà l’asteroide della fascia principale 16 Psyche dopo un viaggio di 4 anni (previsto flyby con Marte nel 2026). L’asteroide, composto principalmente da ferro e nichel, è sospettato di essere il resto di nucleo di un antico pianeta, interessante per capire la formazione ed evoluzione del nostro sistema solare. A bordo anche 30 kg di strumentazione scientifica tra cui Escape and Plasma Acceleration+ Dynamics Explorers (EscaPADE) che studierà l’atmosfera marziana, Janus, che studierà gli asteroidi binari, una camera multispettrale per distinguere metalli e silicati, spettrometro a raggi gamma e a neutroni per la mappatura superficiale, antenna e magnetometro.


In 2024, Starship‘s fifth launch from Boca Chica, Texas at 2.25pm. a very successful test for Spacex which managed to recover the first stage, the 70 meter high Superheavy as it returned to the ground with the aid of mechanical arms. Let’s enjoy the video!
Nel 2024 quinto lancio di Starship da Boca Chica in Texas alle 14:25. un test di grande successo per Spacex che è riuscita a recuperare il primo stadio, il Superheavy alto ben 70 metri mentre rientrava a terra con l’ausilio di bracci meccanici. Gustiamoci il video!
To receive the Astronomy Bulletin Of the Day in your inbox, please put your email address on the contact form: https://abod.blog/contacts/
Per ricevere il bollettino per gli astronaviganti giornaliero nella tua posta elettronica, inserisci la tua mail nel form contatti: https://abod.blog/contacts/
Text, images and video source: Wikipedia, NASA, Asitv
Sostieni anche tu Wikipedia
Google translate
